Farm School
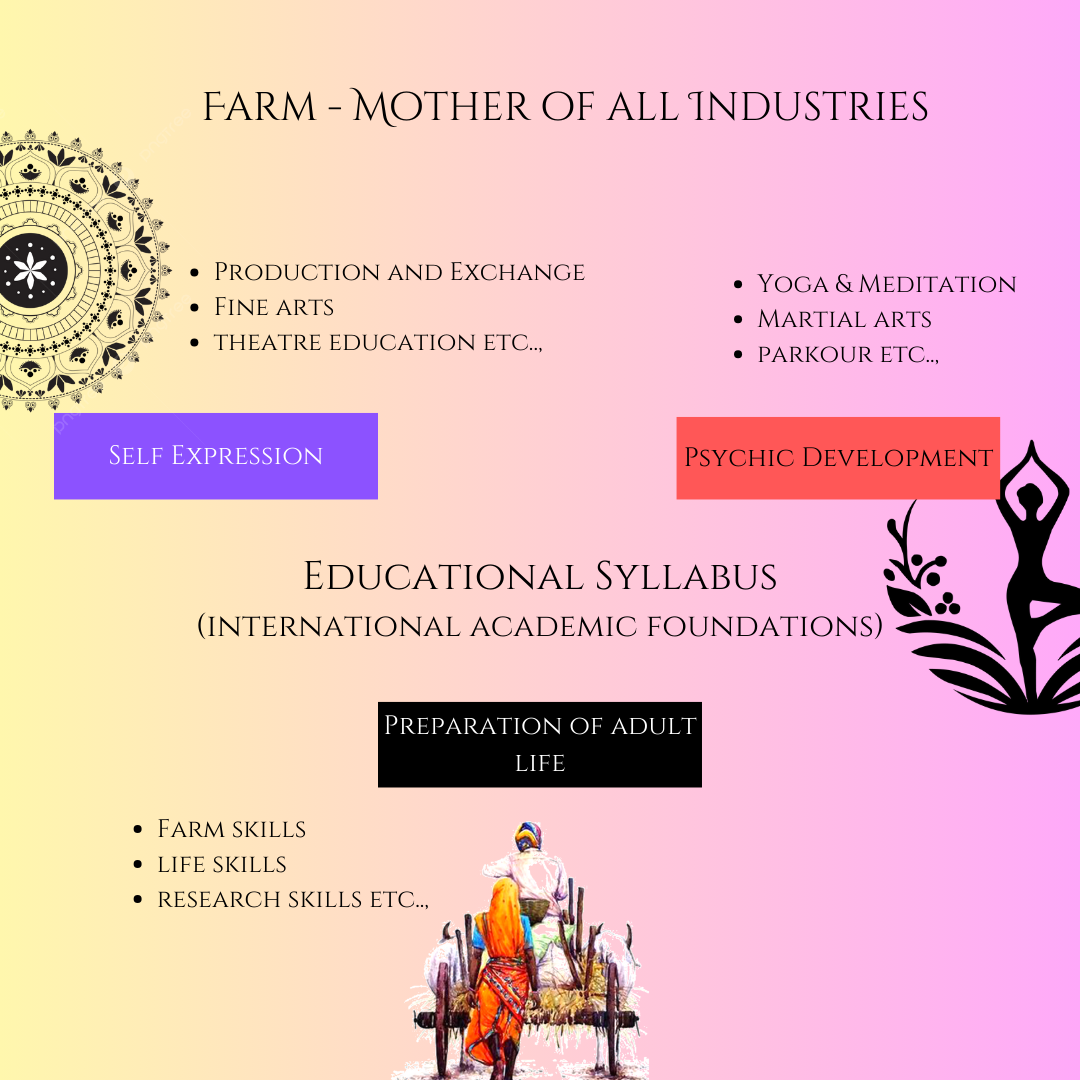
A Montessori Farm School is a unique learning environment that blends Montessori principles with hands-on experiences in nature, fostering independence, responsibility, and a deep connection to the environment. Children engage in activities like organic farming, gardening, and caring for animals while applying academic concepts to real-life scenarios. The school emphasizes sustainability through eco-friendly practices such as composting, water conservation, and renewable energy use. Cultural integration is a key focus, with children exploring traditional crafts, folk music, and local festivals. With child-friendly classrooms, a land laboratory, a herbal garden, and a cultural center, the Montessori Farm School provides a holistic education that nurtures physical, intellectual, and emotional growth. It is a place where children learn to live harmoniously with nature while developing life skills and a strong sense of community.
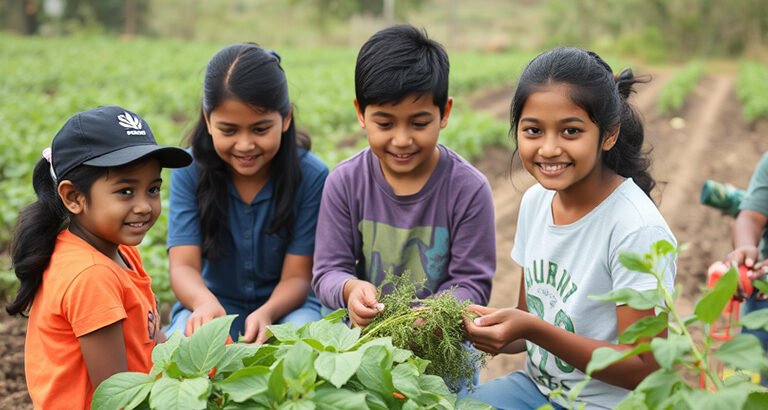

Agriculture and Sustainability
Students learn about organic farming, soil science, composting, animal care, and sustainable practices. They engage in planting, harvesting, and caring for crops and livestock, understanding the cycles of nature and food production.
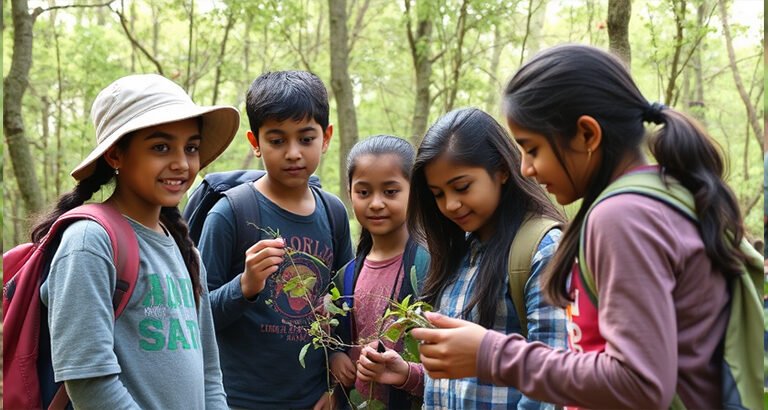

Environmental Science and Ecology
Through exploring local ecosystems, students study biodiversity, conservation, weather, and the impact of human activities on the environment. This builds a sense of responsibility and stewardship for the planet.

Practical Life and Community Skills
Working on a farm fosters cooperation, responsibility, and self-reliance. Students take part in daily chores, manage resources, and learn skills like budgeting, planning, and decision-making, encouraging independence and teamwork.
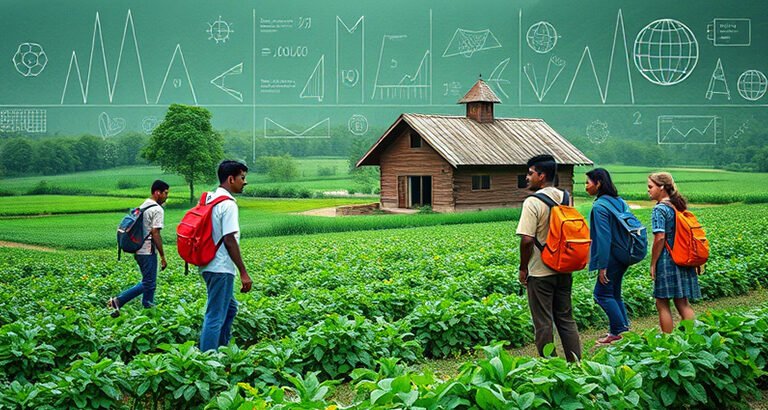

Mathematics and Language Integration
Math is applied to farm tasks, such as measuring, calculating yields, and managing resources, while language skills develop through research, journaling, presentations, and storytelling, connecting academic concepts to practical experiences.
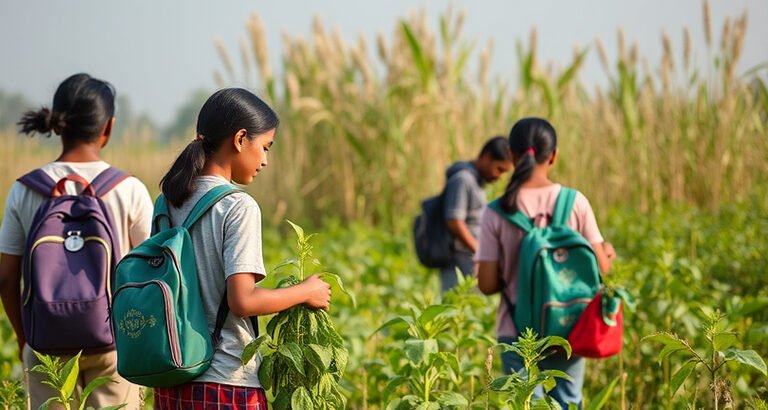

Cultural and Social Studies
Students explore traditional agricultural practices, indigenous knowledge, and cultural connections to the land, learning the history of local farming, traditional crafts, and folk practices.

Physical Development and Outdoor Skills
Time on the farm promotes physical fitness through outdoor work, sports, and activities like hiking, orienteering, and gardening, enhancing strength, coordination, and endurance.
| Key Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Program Objectives | |
| Hands-on Learning | Engage students in agricultural activities to develop practical skills, responsibility, and a connection with nature. |
| Sustainability Education | Teach principles of sustainable farming, waste management, water conservation, and renewable energy use. |
| Cultural Appreciation | Introduce students to Tamil agrarian traditions, indigenous farming practices, traditional crops, and agricultural festivals. |
| Holistic Development | Foster life skills like teamwork, problem-solving, and observation, while promoting physical well-being through farm activities. |
| Key Components of the Program | |
| Organic Farming | |
| Crop Cultivation | Grow traditional crops like rice, millets, pulses, and native vegetables. |
| Seasonal Farming | Plan farming activities based on local Tamil Nadu cropping seasons (e.g., 'Kuruvai', 'Samba', 'Navarai'). |
| No-Chemical Approach | Use organic methods like composting, vermiculture, and green manure. |
| Livestock Management | |
| Native Breeds | Raise indigenous cattle, poultry, and goats, teaching animal husbandry and the benefits of preserving native breeds. |
| Dairy Farming | Offer insights into traditional practices of milk production, ghee making, and curd preparation. |
| Agro-Forestry and Herbal Garden | |
| Native Trees | Plant traditional fruit-bearing trees and medicinal herbs to maintain biodiversity. |
| Herbal Education | Teach the medicinal properties of local herbs, echoing Tamil Siddha practices. |
| Water Conservation | |
| Traditional Irrigation | Demonstrate techniques like 'oorani' (village ponds) and 'eri' (tanks). |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Install systems to collect and utilize rainwater, emphasizing sustainable water use. |
| Composting and Waste Management | |
| Zero Waste | Set up composting systems to recycle farm waste and reduce environmental impact. |
| Program Outcomes | |
| Enhanced Agricultural Knowledge | Students learn sustainable farming methods, environmental care, and traditional farming practices. |
| Improved Life Skills | Students build teamwork, leadership, and responsibility while actively participating in farm activities. |
| Sense of Responsibility | Develop a connection to the land and understanding of food production, instilling responsibility for nature's resources. |
Practical Sessions in the Land Laboratory
| Key Areas | Details |
|---|---|
| Local Crop Cultivation | |
| Seasonal Planting: Students participate in planting, tending, and harvesting local crops like paddy, millets, pulses, and native vegetables. They learn about the planting calendar, soil preparation, and traditional agricultural practices. | |
| Seed Saving: Teach students the importance of preserving indigenous seeds, conducting seed collection, cleaning, and storage activities. Crop Rotation and Companion Planting: Introduce sustainable farming practices like crop rotation to improve soil fertility and companion planting to manage pests naturally. |
|
| Organic Farming Techniques | Soil Health: Hands-on sessions on testing soil quality, improving soil fertility using compost and natural amendments, and understanding the role of microorganisms. |
| Composting: Demonstrate composting techniques using farm waste, leaves, and organic materials. Students can maintain compost bins and learn how to create nutrient-rich fertilizers. | |
| Natural Pest Control: Practical learning on using herbal mixtures and biological agents to manage pests, avoiding chemical pesticides. Introduce traditional Tamil methods of pest management like 'panchakavya' and neem-based sprays. | |
| Nature Conservation and Eco-friendly Practices | Tree Planting and Agro-Forestry: Plant native trees and shrubs to create windbreaks, support biodiversity, and teach students about the benefits of agroforestry. |
| Water Conservation Projects: Students can participate in setting up drip irrigation systems, rainwater harvesting structures, and learn about efficient water use. | |
| Pollinator Gardens: Develop gardens with flowering plants to attract bees, butterflies, and other pollinators, educating students on the importance of pollination in agriculture. | |
| Field Observation and Data Collection | Growth Monitoring: Students regularly monitor the growth of plants, recording data on germination rates, pest attacks, and yields. This fosters scientific observation skills and an understanding of plant life cycles. |
| Biodiversity Surveys: Conduct surveys to observe and record different species of plants, insects, and birds found in and around the farm, teaching ecosystem interdependence. | |
| Soil and Water Testing: Practical activities to test soil pH, nutrient content, and water quality, enhancing their understanding of environmental science. | |
| Workshops on Traditional Tamil Agrarian Practices | Herbal Planting and Usage: Teach how to grow and use herbs like 'tulsi,' 'neem,' and 'karisalankanni' that have been traditionally used in Tamil culture for medicinal purposes. |
| Millet Processing: Conduct sessions on traditional millet processing techniques, grinding methods, and preparing millet-based foods. | |
| Traditional Irrigation Systems: Educate students on historical irrigation techniques used in Tamil Nadu, such as tank systems ('eri') and 'kudimaramathu' (community water management). | |
| Integrated Farm Projects | Vegetable Gardens and Edible Landscaping: Students design and maintain vegetable patches, herb spirals, and fruit orchards, applying principles of permaculture. |
| Farm to Table Program: Practical sessions where students harvest produce, learn to cook simple traditional dishes, and understand the importance of fresh, local food. | |
| Small-Scale Animal Husbandry: Caring for animals like chickens, goats, and cows, understanding their role in a sustainable farming system (e.g., manure for fertilization). | |
| Learning Outcomes | Knowledge of Local Agriculture: Students gain a deep understanding of local crops, traditional farming methods, and sustainable practices. |
| Ecological Responsibility: Hands-on activities instill a sense of environmental stewardship and the importance of conserving natural resources. | |
| Practical Life Skills: Through planting, composting, and caring for animals, students develop skills that enhance their confidence, independence, and teamwork. |

Land Laboratory
The Land Laboratory is a dynamic, hands-on learning space that connects children to the environment, Tamil traditions, and sustainable living practices. Here, children engage in growing local crops like paddy, millets, pulses, and vegetables through practical activities such as soil preparation, sowing, and harvesting, all while learning organic farming techniques and composting. They also explore nature conservation by planting trees, creating biodiversity zones, and studying indigenous flora and fauna. Traditional Tamil farming practices are integrated into the curriculum, including lessons on crop rotation, natural pest control using herbs, and the significance of the Tamil farming calendar. The Land Laboratory features a seed bank for preserving and studying heirloom seeds, promoting biodiversity, and a herbal garden where children grow medicinal plants, gaining insight into Tamil Siddha medicine. Through these immersive experiences, the Land Laboratory fosters environmental stewardship, cultural appreciation, and sustainable practices.
Daily menu signs are posted at the beginning of all meal lines. Items offered as a part of lunch are listed within the grain, protein, milk, fruit and vegetable spaces on the menu board.
Daily menu signs are posted at the beginning of all meal lines. Items offered as a part of lunch are listed within the grain, protein, milk, fruit and vegetable spaces on the menu board.